IEEE 802.1X Stanrd - CompTIA Security +
Hola,
I try to navigate around concepts and names, and I found it hard to get around long ones, but if they include numbers, well, that's a different story! Here I am again, testing my knowledge, and I found that 802.1X wasn't clear to me. This time, neither Mr. Dion's nor Messer's tutorials or sources helped me... (¬_¬”)
It's not you guys, it's me. I found a video in Spanish full of these long acronyms that provided me with a good overview. In this case, I found this video if you don't speak Spanish no problemo...here are my notes ʕ ◕ᴥ◕ ʔ
This time, I took note of the video and did have to find a bit more refined or concrete info, as it might sound a bit imprecise to write on a blog. Again, Mr. Fernando, great job! OK, let's delve deeper into it.

802.1X IEEE standard for port-based network access control (PNAC).Authenticates devices before granting network access, ensuring only authorized devices communicate. Supplicant Device (e.g., laptop) requesting network access. Authenticator Network device (e.g., switch, access point) controlling access by blocking/unblocking the port. Authentication Server Verifies Supplicant credentials, typically using RADIUS.
- Wait, I didn't use AI yet... i am afraid this could be to much text let me add this visual here.
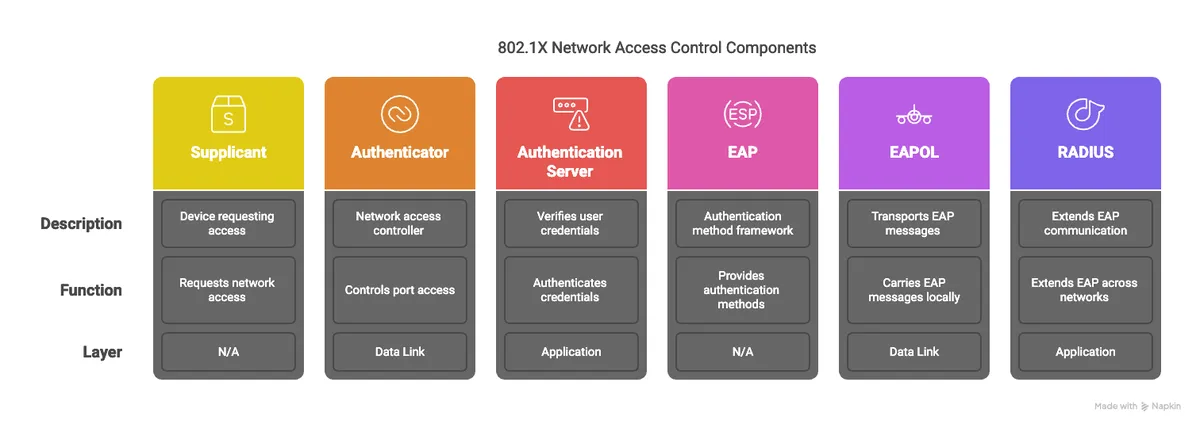
EAP Authentication Overview
Key Protocols
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
- A flexible framework for authentication methods.
- Examples:
EAP-TLS,PEAP.
EAPOL (EAP over LAN)
- Transports
EAPmessages between theSupplicantandAuthenticator. - Operates at the data link layer (Layer 2).
- Transports
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service)
- Protocol for communication between the
AuthenticatorandAuthentication Server. - Operates at the application layer (Layer 7).
- Protocol for communication between the
Authentication Process
- The
Supplicantsends credentials viaEAPOLto theAuthenticator. - The
AuthenticatorforwardsEAPmessages to theAuthentication ServerusingRADIUS. - The
Authentication Serververifies credentials and notifies theAuthenticator. - If successful, the
Authenticatorunblocks the port for access.
Protocol Interaction
EAP: Provides the authentication framework.EAPOL: CarriesEAPmessages locally betweenSupplicantandAuthenticator(Layer 2).RADIUS: ExtendsEAPcommunication across networks to theAuthentication Server(Layer 7).
Security Structure
- Components:
Supplicant,Authenticator,Authentication Server. - The port remains blocked until authentication is complete.
- Ensures secure and controlled network access.
I also used AI to style fast and furious this note in markdown, so i THINK is fair to add my usual last label here:
